数据结构与算法学习笔记01

程序=数据结构+算法。
浙江大学数据结构是国家精品课程,于2018年3月开学,2018年6月学期结束。
<!--more-->实验1:给出数字N,要求程序输出1~N的整数
使用Java测试:输出10000次,for循环耗时114ms,递归耗时61ms!100000次递归栈溢出崩溃,for循环耗时900ms。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// write your code here
Main m = new Main();
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
m.printN(10000);
System.out.println("time="+(System.currentTimeMillis()-time));
time = System.currentTimeMillis();
m.printNR(10000);
System.out.println("time="+(System.currentTimeMillis()-time));
}
private void printNR(int n) {
if(n>0) {
printNR(n - 1);
System.out.println(n);
}
}
private void printN(int n){
for(int i= 1;i<=n;i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
用C测试:输出100000次,for循环耗时149ms,递归耗时148ms,100000次递归耗时150ms,100万次
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
void printN(int n);
void printNC(int n);
int main(){
clock_t startTime = clock();
printN(100000);
//double diff = ;
printf("%f seconds\n",difftime(clock(),startTime)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
}
void printN(int n){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
printf("%d\n",i);
}
}
void printNC(int n){
if(n){
printNC(n-1);
printf("%d\n",n);
}
}
- 总结:
C语言程序运行效率至少在Java的10倍以上(C程序计时不准,需要重新测试)- 递归的空间效率很差,容易堆栈溢出崩溃。
- Java环境递归耗时是for循环的1/2。
- C语言环境递归耗时和for循环差不多。
实验2:计算多项式的值
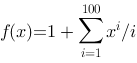
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// write your code here
Test02 t = new Test02();
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<100000;i++) {
t.f1(1.1);
}
System.out.println("time=" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - time));
time = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<100000;i++) {
t.f2(1.1);
}
System.out.println("time=" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - time));
}
private double f1(double x) {
double v = 1f;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
v += Math.pow(x,i) / i;
}
return v;
}
//f(x) = 1+x(1/1+x(1/2+x(1/3+....x(1/100))))
private double f2(double x) {
double v = x/100;
int i = 100;
while (i>1) {
v = x*(1f/(i-1)+v);
i--;
}
return v+1;
}
}
- 总结:
- 循环10万次测试,方法1,耗时1016ms,方法2耗时16ms。约100倍的效率差距
- 计算时一定要注意,整形和浮点型
v = x*(1f/(i-1)+v); - 方法1,慢就慢在
pow函数上 - 替换pow函数为计数循环
x *=x耗时500ms,差距缩小至约20倍。
作业1
01-复杂度1 最大子列和问题(20 分) 给定K个整数组成的序列{ N1, N2, ..., NK},“连续子列”被定义为{ Ni, Ni+1, ..., Nj},其中 1≤i≤j≤K。 “最大子列和”则被定义为所有连续子列元素的和中最大者。 例如给定序列{ -2, 11, -4, 13, -5, -2 },其连续子列{ 11, -4, 13 }有最大的和20。 现要求你编写程序,计算给定整数序列的最大子列和。
本题旨在测试各种不同的算法在各种数据情况下的表现。
各组测试数据特点如下:
数据1:与样例等价,测试基本正确性; 数据2:102个随机整数; 数据3:103个随机整数; 数据4:104个随机整数; 数据5:105个随机整数; 输入格式:
输入第1行给出正整数K (≤100000);第2行给出K个整数,其间以空格分隔。
输出格式:
在一行中输出最大子列和。如果序列中所有整数皆为负数,则输出0。
输入样例:
6
-2 11 -4 13 -5 -2
输出样例:
20
实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int k = scanner.nextInt();
int[] n = new int[k];
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if (scanner.hasNext()) {
n[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println(maximumSubsequenceSum(n));
}
/**
* 在线处理算法,任意时刻给出的都是当前最大子数列和
* @param n
* @return
*/
private static int maximumSubsequenceSum(int[] n) {
int thisMax = 0;
int maxSum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n.length; i++) {
thisMax += n[i];
if (thisMax < 0) {
thisMax = 0;
} else if (thisMax > maxSum) {
maxSum = thisMax;
}
}
return maxSum;
}
}
作业2
01-复杂度2 Maximum Subsequence Sum(25 分) Given a sequence of K integers { N1, N2, ..., NK}. A continuous subsequence is defined to be { Ni, Ni+1, ..., Nj } where 1≤i≤j≤K. The Maximum Subsequence is the continuous subsequence which has the largest sum of its elements. For example, given sequence { -2, 11, -4, 13, -5, -2 }, its maximum subsequence is { 11, -4, 13 } with the largest sum being 20.
Now you are supposed to find the largest sum, together with the first and the last numbers of the maximum subsequence.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case occupies two lines. The first line contains a positive integer K (≤10000). The second line contains K numbers, separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, output in one line the largest sum, together with the first and the last numbers of the maximum subsequence. The numbers must be separated by one space, but there must be no extra space at the end of a line. In case that the maximum subsequence is not unique, output the one with the smallest indices i and j (as shown by the sample case). If all the K numbers are negative, then its maximum sum is defined to be 0, and you are supposed to output the first and the last numbers of the whole sequence.
Sample Input:
10
-10 1 2 3 4 -5 -23 3 7 -21
Sample Output:
10 1 4
- 实现:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String countString = null;
String numbersString =null;
try {
countString = reader.readLine();
numbersString = reader.readLine();
}catch (Exception ignored){
}
int[] n = new int[Integer.parseInt(countString)];
String[] numbersStringArray = numbersString.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < n.length; i++) {
n[i] = Integer.parseInt(numbersStringArray[i]);
}
// Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// int k = scanner.nextInt();
// int[] n = new int[k];
//
// for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
// n[i] = scanner.nextInt();
// }
maximumSubsequenceSum(n);
}
/**
* 在线处理算法,任意时刻给出的都是当前最大子数列和
*
* @param n
* @return
*/
private static void maximumSubsequenceSum(int[] n) {
int thisMax = 0;
int maxSum = 0;
int startI = 0;
int endI = n.length - 1;
int temp = 0;
boolean isMaxStart = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n.length; i++) {
thisMax += n[i];
if (thisMax < 0) {
thisMax = 0;
temp = 0;
isMaxStart = true;
} else {
if(isMaxStart){
temp = i;
isMaxStart = false;
}
if (thisMax > maxSum) {
maxSum = thisMax;
endI = i;
startI = temp;
}
if(maxSum==0){
startI =temp;
endI = i;
}
}
}
System.out.println(maxSum + " " + n[startI] + " " + n[endI]);
}
}
- 总结
- 这题所有case要求在200ms内执行完毕,其中一个case比较大的N导致执行超时,调查发现Scanner这个东西贼慢...换成BufferReader就好了。
作业3
01-复杂度3 二分查找(20 分) 本题要求实现二分查找算法。
函数接口定义:
Position BinarySearch( List L, ElementType X );
其中List结构定义如下:
typedef int Position;
typedef struct LNode *List;
struct LNode {
ElementType Data[MAXSIZE];
Position Last; /* 保存线性表中最后一个元素的位置 */
};
L是用户传入的一个线性表,其中ElementType元素可以通过>、==、<进行比较,并且题目保证传入的数据是递增有序的。函数BinarySearch要查找X在Data中的位置,即数组下标(注意:元素从下标1开始存储)。找到则返回下标,否则返回一个特殊的失败标记NotFound。
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXSIZE 10
#define NotFound 0
typedef int ElementType;
typedef int Position;
typedef struct LNode *List;
struct LNode {
ElementType Data[MAXSIZE];
Position Last; /* 保存线性表中最后一个元素的位置 */
};
List ReadInput(); /* 裁判实现,细节不表。元素从下标1开始存储 */
Position BinarySearch( List L, ElementType X );
int main()
{
List L;
ElementType X;
Position P;
L = ReadInput();
scanf("%d", &X);
P = BinarySearch( L, X );
printf("%d\n", P);
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例1:
5
12 31 55 89 101
31
输出样例1:
2
输入样例2:
3
26 78 233
31
输出样例2:
0
- 实现:
 青衿AI
青衿AI